eSignature
As organizations go paperless, there is an increased requirement for compliant approval of batch records, quality procedures or change controls. Traditionally these requirements were satisfied with wet ink signatures, but that doesn't work in the factory of the future. That's why the eSignature was invented, the digital twin of the wet ink signature.
This article presents how AlisQI provides support for eSignatures, and how you can add eSignature fields to your quality processes.
In this article
What is an eSignature?
An electronic signature is a digital means to validate one's identity prior to confirming or performing a certain action.
In the context of a QMS this can be interpreted as the validation that one is indeed the individual they pretend to be, prior to approving a quality record or quality procedure.
This means that the consumer of the data, records or procedures can be assured that the approval is trustworthy.
With a "traditional" text field or checkbox, this cannot be guaranteed. A proper eSignature control can be considered the notary in your QMS.
eSignature requirements
The regulatory requirements to an eSignature might differ per regulation. In this article we highlight the most common and important
Technical requirements
In order to be compliant electronic signatures must include:
- The printed name of the signer
- The date and time the signature was executed
- Digital adopted signature
- The meaning of the signature (the labeled “signing reason”)
Furthermore, a signature must be unique to an individual. And electronic signatures that are not based upon biometrics must employ at least two distinct identification components such as an identification code plus a password.
Organizational requirements
Besides these technical requirements, the eSignature control needs to be embedded in a procedural foundation to give it all the legal value your organization needs for them to have. This might vary per industry, organization and process.
- Persons using electronic signatures shall, prior to or at the time of such use, agree that the electronic signatures in their system are intended to be legally binding equivalent of traditional handwritten signatures.This might be something to include in a labor contract or HR handbook.
- Identification code and password issuances must be periodically checked, recalled or revise.
This is something that can be managed in an Authentication Provider like Azure AD. - A procedure must be in place for initial and periodic testing of devices such as tokens or cards that bear or generate identification code or password information to ensure that they function properly and have not been altered in an unauthorized manner.
eSignature in AlisQI
AlisQI supports eSignatures in all forms. There is a dedicated eSignature field type that users can add to their forms. These eSignature fields can be used in workflows, reporting and expressions as any other field type.
Add signature field
In AlisQI you can add eSignature fields to any form. This works similar to adding a text or numeric field.
Use the label field to define the signing reason.
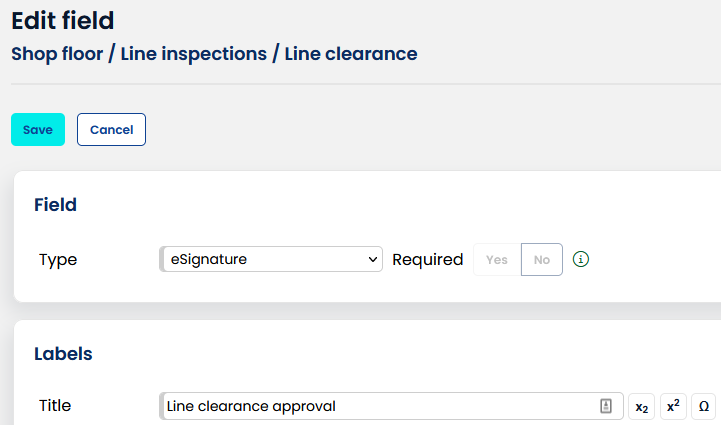
The eSignature fields behave as any other field in AlisQI. This means that they can be used in filters, workflows, reporting and expressions. The only exception is the API and data import. eSignature fields are not available for data entry via the API or (Excel) data import.
Signing
The signing process is:
- User opens a form and fills in the (relevant) fields
- User clicks the signature field checkbox to express their intend to sign.
The "Save" button in the toolbar changes to depict the intend to sign.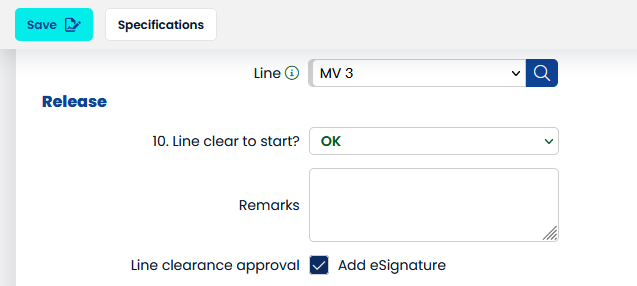
- User click "Save"
- System requests user to confirm their identity.
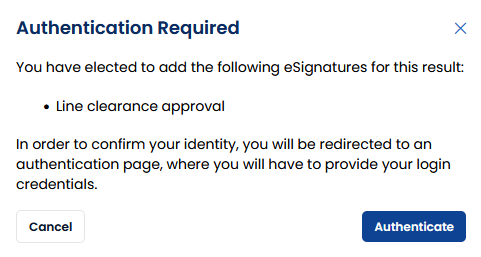
- The user is required to input their login credentials to confirm their identity. When Single Sign On is enabled, users will be forwarded to the login screen of the SSO Authentication provider.
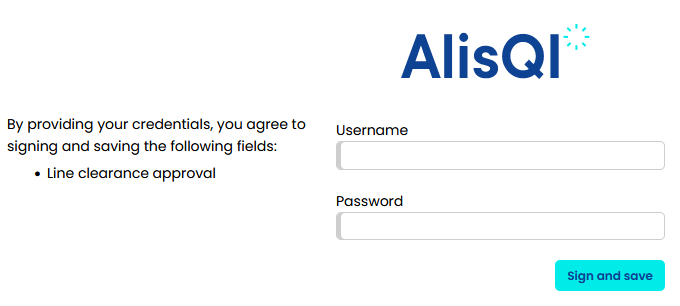
- System validates identity:
- If the authentication is positive the data is stored and the signature is stored
- If the authentication is negative, the data is stored but the signature is not.
Once a signature field is signed, it cannot be changed or unset.
Signature reporting
The signature is reported in both the results overviews as well as in the audit trail.
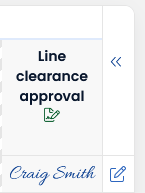
Clicking on a eSignature value, provides you with a popup with details on the sign action and signee.
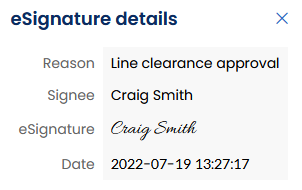
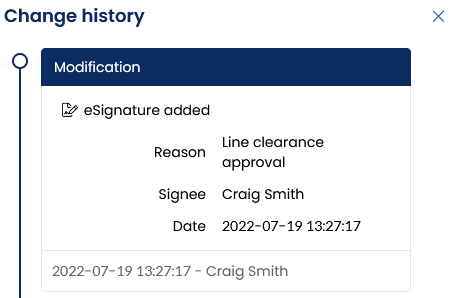
Audit trail
The audit trail also explicitly mentions the sign actions in the change history of a result.
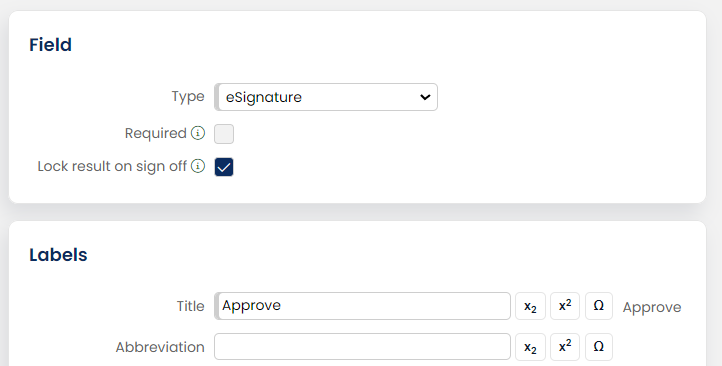
Lock results by sign-off
By checking the "Lock result on sign off" checkbox, the result will be locked for editing or deletion by any means (including workflow or API).
Circumvent the locking mechanism
There is no way for users to circumvent the eSignature locking mechanism. If for any reason the data should be altered after sign off, system administrators can "bypass" the locking mechanism by temporarily uncheck this "Lock result on sign off" checkbox. After the changes, the locking mechanism can be restored.